Venous Thromboembolic Disorder Treatment in Bandlaguda
Venous thromboembolic disorders or VTE is an umbrella term for a spectrum of conditions characterized by the formation of blood clots within the veins that pose significant health risks. There are numerous factors that contribute to the development of VTE including immobility, surgery, trauma, genetic predisposition, and certain medical conditions. Understanding the risk factors that trigger this condition is crucial for both prevention and early intervention. Individuals undergoing surgery or those with prolonged immobility such as during long flights, are particularly susceptible to this disorder. Genetic factors such as mutations in clotting-related genes can also increase the likelihood of developing VTE.
DVT, or deep vein thrombosis, and pulmonary embolism (PE) are both primary components of venous thromboembolism.
Deep Vein Thrombosis: DVT is a condition characterized by the formation of blood clots, or thrombi, in the deep veins of the body, usually in the legs. DVT often occurs due to factors like prolonged immobility, surgery, trauma, genetic predisposition, or certain medical conditions that affect blood clotting.
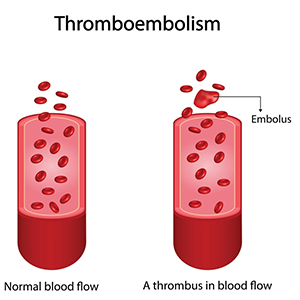
Pulmonary Embolism: PE occurs when a blood clot, typically originating from the deep veins of the legs (DVT), breaks loose and travels to the lungs, causing a blockage in the pulmonary arteries. The most common cause of PE is the migration of a blood clot from the legs, but clots can also originate in other parts of the body.
Systemic Thrombolysis: Systemic thrombolysis is a medical treatment that involves the administration of clot-dissolving medications by Best interventional cardiologist in attapur into the bloodstream to dissolve blood clots in various parts of the body. This medical intervention is commonly used to address serious conditions such as pulmonary embolism, acute ischemic stroke, or other instances where rapid clot dissolution is necessary to prevent severe complications.
IVC filter placement : IVC filter placement refers to the insertion of an inferior vena cava (IVC) filter into the large vein that carries deoxygenated blood from the lower half of the body back to the heart. The inferior vena cava filter is a small, cage-like device designed to catch and prevent blood clots from traveling to the lungs and causing pulmonary embolism. This procedure is often considered for individuals at risk of developing blood clots, especially those who cannot tolerate or have failed anticoagulant therapy. Common scenarios include patients with deep vein thrombosis (DVT) or other conditions that predispose them to venous thromboembolism.
For more details on Venous Thromboembolic Disorders treatment, consult Dr. Naresh Kumar Monigari
